How to modify any page with JavaScript to improve a website’s SEO.

JavaScript is often mentioned in SEO in relation to WPO improvements or rendering issues. It’s also frequently discussed because doing SEO on JavaScript frameworks requires a different approach and a higher-than-average level of knowledge.
However, the characteristics and advantages of using JavaScript—and how we can leverage it to improve or modify any aspect of our website as a sort of “patch”—are not usually emphasized.
In this article, I’ll explain everything from the beginning and show you how to use JavaScript to change virtually any website, why it works, and how to do it with a moderately advanced understanding. I’ll also share, at the end, a trick to apply this to any website in a scalable way, regardless of your SEO or programming level.
By default, JavaScript is a client-side language. This means it runs on the user’s device (specifically, their browser), not on the hosting server. In other words, it’s the visitor’s computer or mobile device that executes the code and makes the necessary modifications.
This also increases the load and resource usage for anyone crawling the page, since the responsibility falls on the user. That’s why crawling a website with JavaScript takes longer than without it, which is key to understanding how Google handles it—time is resources and money. (By the way, Ahrefs has been crawling with JS since 2018.)
JavaScript also allows users to interact with the webpage thanks to running on the client side.
To put it simply, JavaScript can be thought of as a “patch language.” The server first delivers all files: HTML, CSS, JS, and multimedia.
Once the HTML structure reaches the user, their browser begins executing the JavaScript as instructed in the HTML. The scripts then interact with and modify the HTML code.
Think of the HTML you receive as the DOM, which is what you see when you press CTRL+U or view-source on a URL you’re inspecting.
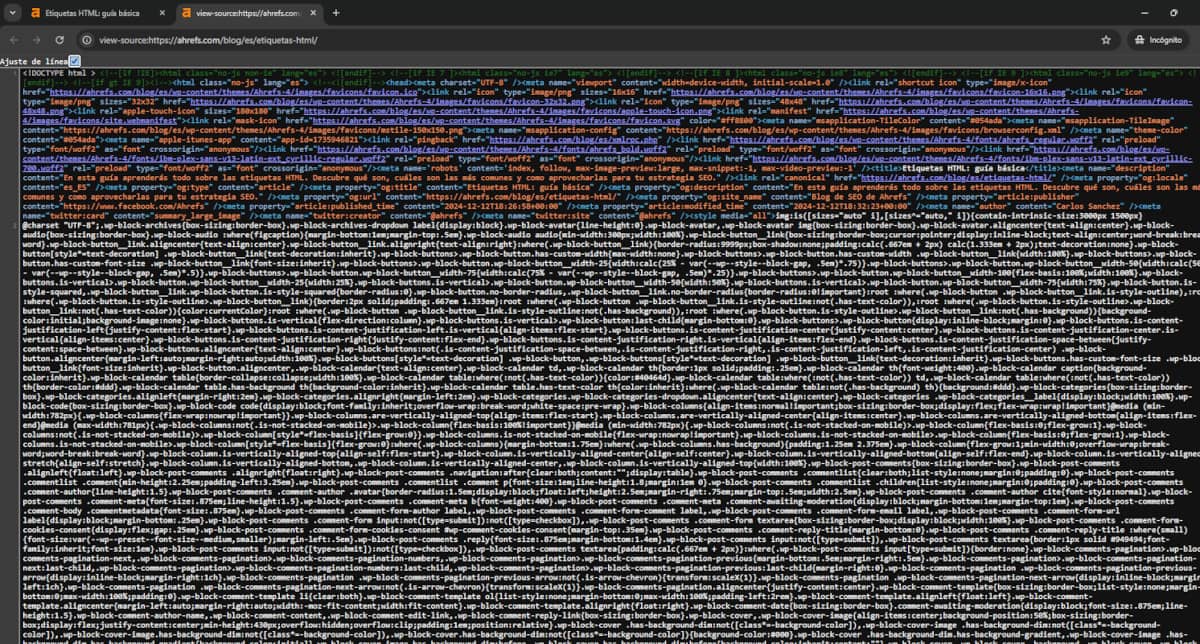
However, this code isn’t necessarily the same as what you see in the browser’s element inspector:
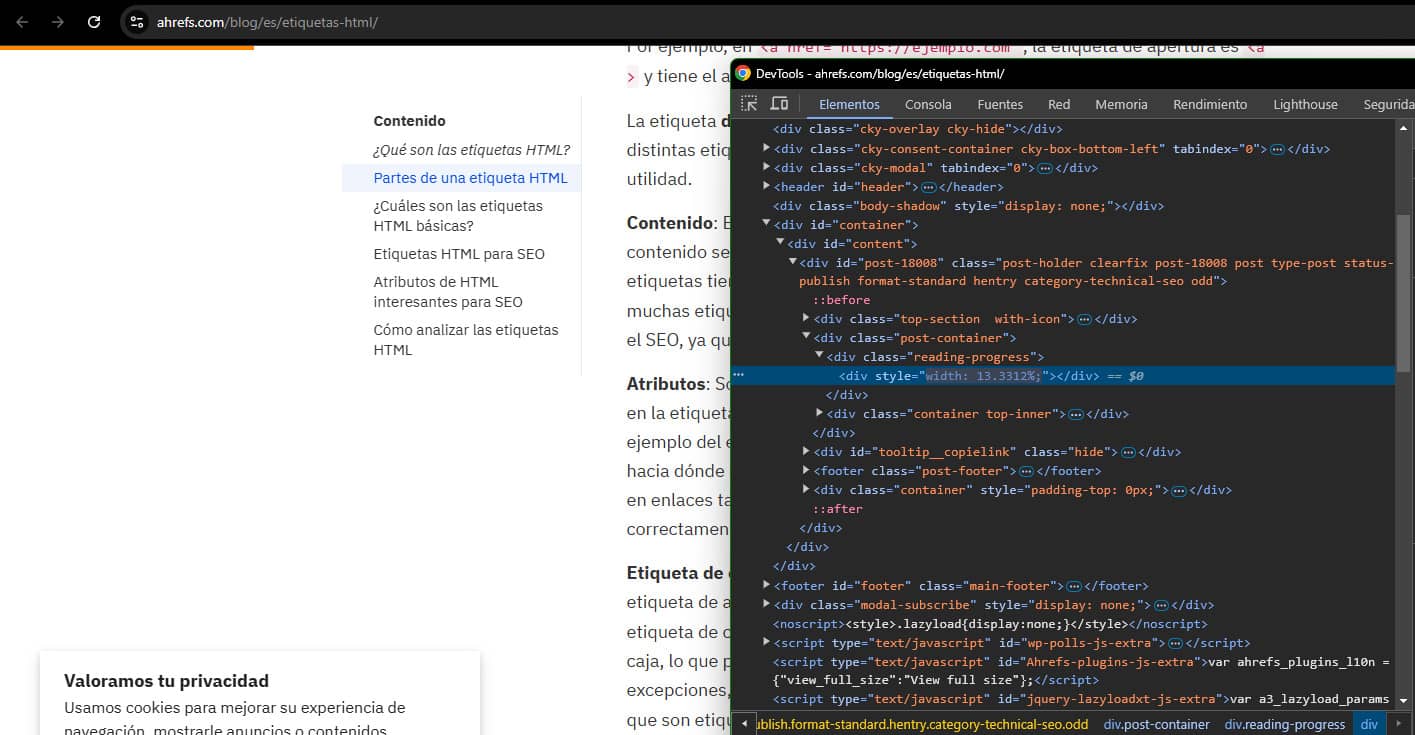
Since JavaScript can modify the HTML of a website, it’s extremely useful for SEOs to change content that would otherwise be unchangeable.
If these changes are executed “quickly” via JavaScript, Google will be able to process them.
To check whether Google processes changes correctly, we can use the URL Inspection tool in Search Console. If you don’t have access, you can use the Google Structured Data Tester. Even though it wasn’t designed for this purpose, you can also see the final HTML using Ahrefs’ Page Inspect tool.

While Google can render and process JavaScript, there are some important aspects to keep in mind to fully leverage it.
As mentioned, since JavaScript runs on the client side, we can insert JavaScript and modify a website freely, regardless of the programming language it was built with.
This means that even if a website uses a cookies plugin that adds an H1, or is built with a technology that doesn’t allow code modifications, we can still change and modify the final output.
Certain conditions must be met, which cannot be bypassed with JS alone if they are not fulfilled:
If these conditions are met, Google will attempt to render the URL and will only consider the final DOM, which is typically available roughly 5 seconds after the page loads—so WPO is also important here.
We need a space in the backend or somewhere on our website to load an external JavaScript file, or be able to add script tags via HTML.
It’s important to remember, as mentioned earlier, that for the changes to take effect, the script must execute after the page content has loaded.
How should this be done? If you don’t want to deal with code, you can see it at the end of the article, where I explain how to make these changes without any programming knowledge.
If you know programming or are curious about how it’s done, I’ll explain it here.
In JavaScript, to modify an element, you first need to know how to select it.
Here are examples of how we could modify a link in different ways using JS:
Let’s say we have this link:
With JavaScript, we could do several things:
Remember, if you don’t know how to inject JavaScript into your website, you can check this article on how to modify a website without programming knowledge, or use Tag Manager as I explain after the examples.
// Select the link with the class "example-link" const link = document.querySelector('.example-link'); // Change the text using innerHTML link.innerHTML = 'This is the new Anchor Text';
// Select the link with the class "example-link" const link = document.querySelector('.example-link'); link.outerHTML = `<div class="container">${link.outerHTML}</div>`;
// Select the link with the class "example-link" const link = document.querySelector('.example-link'); link.href = 'https://new-link.com';
// Select the link with the class "example-link" const link = document.querySelector('.example-link'); link.removeAttribute('target');
// Select the link with the class "example-link" const link = document.querySelector('.example-link'); if (link.rel === 'nofollow') { link.rel = 'noopener'; }
As you can see, you can modify almost any element. The only thing you need to know is how to select it and how to change it using JavaScript commands.
This is a real example of a script that replaces headings in the popular OneTrust platform much more easily than through the platform itself. You just need to make sure your script loads after the OneTrust script.
// Select the container element by ID const container = document.getElementById('onetrust-pc-sdk'); if (container) { // Select all h1, h2, h3, h4 headings inside the container const headings = container.querySelectorAll('h1, h2, h3, h4'); headings.forEach(heading => { // Create a new div element const div = document.createElement('div'); // Copy all attributes from the heading to the div Array.from(heading.attributes).forEach(attr => { div.setAttribute(attr.name, attr.value); }); // Copy the content of the heading to the div div.innerHTML = heading.innerHTML; // Replace the heading with the div in the DOM heading.replaceWith(div); }); }
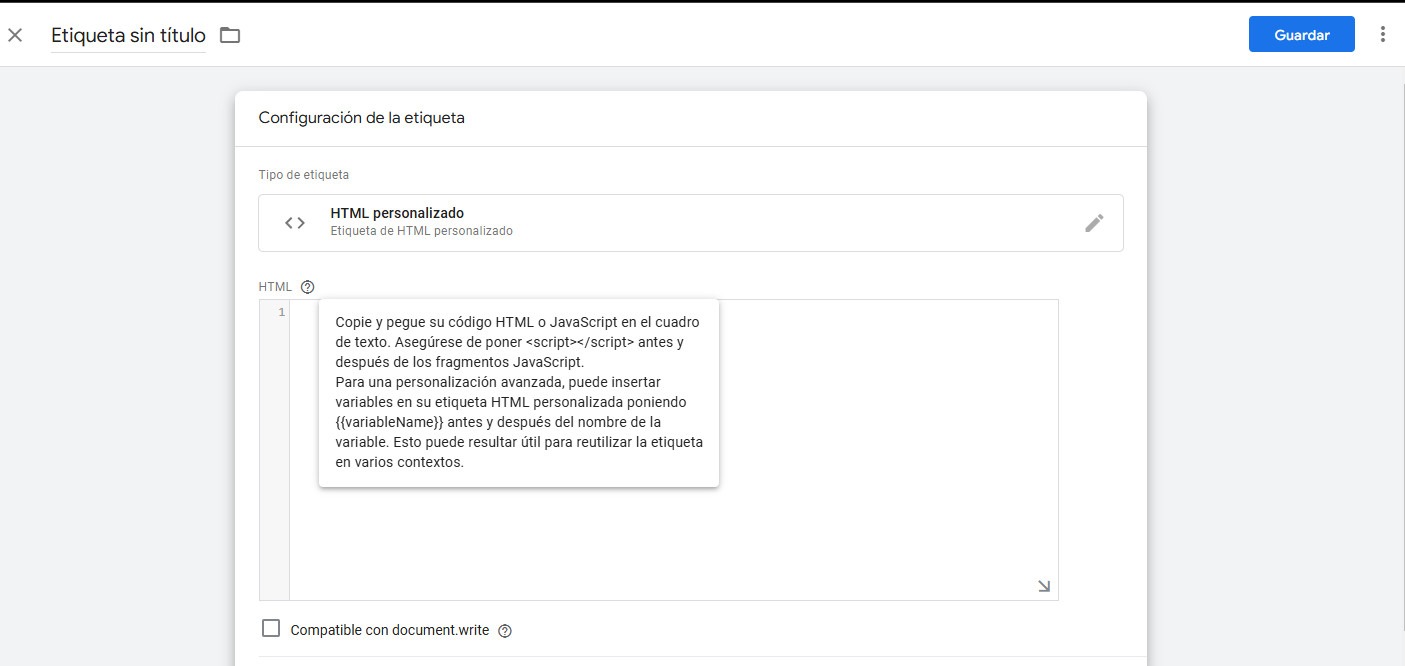
If, for some reason, you don’t know how to modify it directly on the website or don’t have access, you can do it via Tag Manager, as it allows you to insert other scripts and add your own.
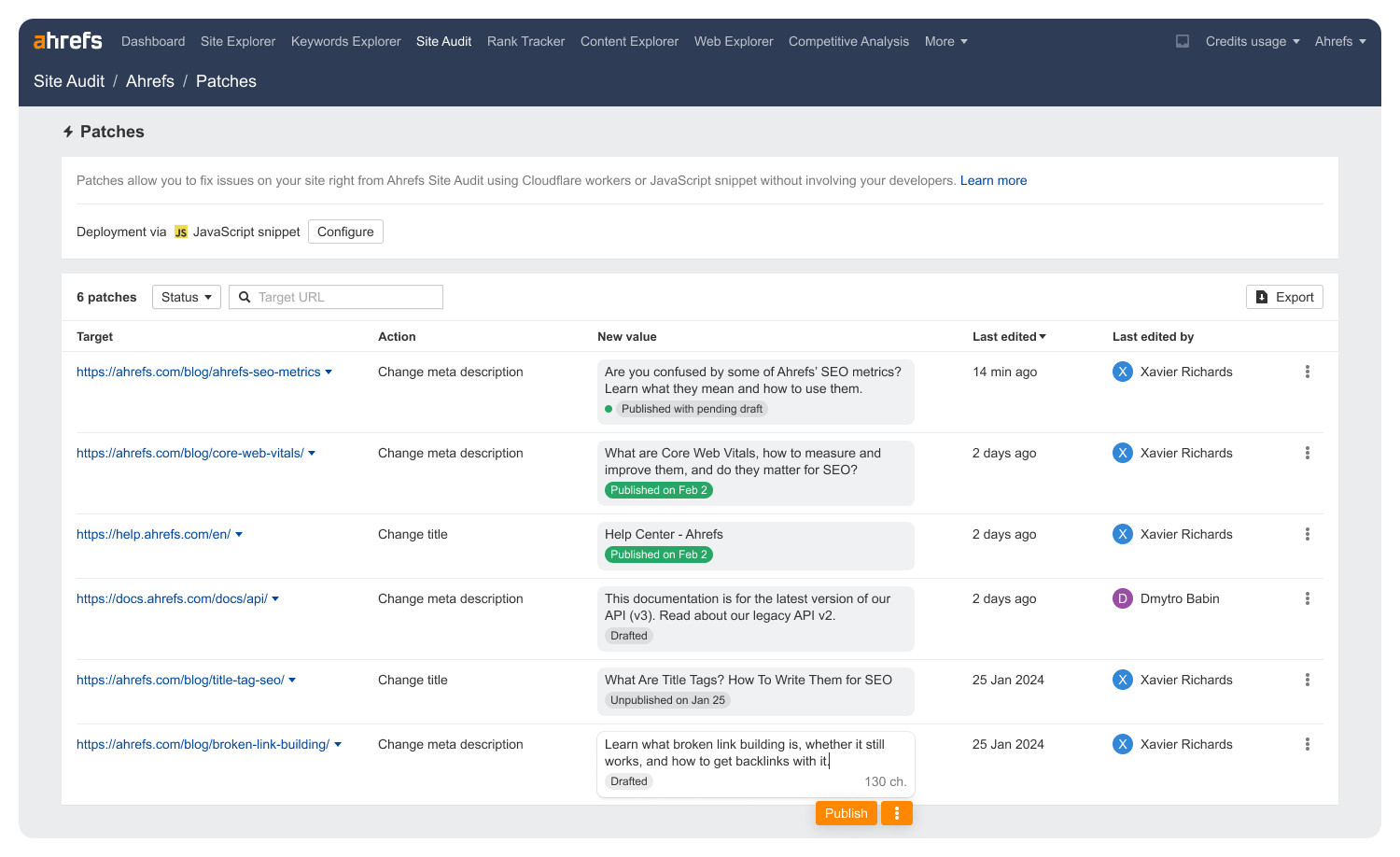
As mentioned earlier, here’s the solution for those who don’t know programming to modify web elements using JavaScript.
With Ahrefs Patches, you can modify elements using the same principle without needing to know JavaScript.
With the Max plan in Ahrefs’ Site Audit section, you can use Patches to modify elements without knowing JavaScript.
The principle and execution are the same, but you don’t have to worry about coding to see the final result.
Thanks to JavaScript and how Google renders websites today, we can modify elements even if the website wasn’t properly programmed or doesn’t allow backend changes. This works regardless of the framework or CMS, saving a lot of time compared to modifying the core code or waiting on IT departments.
Although it’s not perfect—since changes occur when the JS executes and may sometimes cause minor visual issues—it’s a powerful tool or tactic to add to our projects. Any element in any web environment can be modified and is readable by Google, giving us more flexibility when implementing SEO strategies.
I currently offer advanced SEO training in Spanish. Would you like me to create an English version? Let me know!
Tell me you're interested