Key Strategies to Optimize Your Presence in AI and Leverage Its Growing Impact on SEO

SEO has been "killing itself" for some time now, even though Google still dominates general web search.
However, AI is gaining prominence, and some “self-proclaimed gurus” have emerged, claiming to be 'experts' in something that’s barely two years old in LLM SEO (a.k.a. GEO/AIO) or whatever fancy acronyms you choose to invent to define SEO for LLMs (Large Language Models).
Given this, I want to shed some light on strategies that have worked for us with clients, and how we can—or should—work to improve our positioning in artificial intelligence. it’s not just important to be mentioned, but also how you’re portrayed.
To do this, it’s important to understand artificial intelligence. While we nerds like to experiment with alternatives—and although there are many types of AI (visual, conversational, predictive, generative)—the majority of information-based queries are currently dominated by general-purpose LLMs, with ChatGPT undoubtedly being the most widely used. That’s why I’m going to focus on it.
In summary, we could summarize these GEO tasks and their impact:
| Action | Impact on LLMs | Notes |
| Optimize traditional technical SEO (clean HTML, CWV, logical architecture, correct hreflang) | High | Essential foundation; most LLM improvements stem from this. |
| Clear and structured textual content (avoid irony and sarcasm) | High | It helps the LLM understand and reformulate your content well. |
| Mentions of your brand or product on third-party websites (with or without links) | High | Increases the likelihood that the LLM will recognize you as an authority. |
| Well-structured comparisons, tables, and lists | High | LLMs excel at extracting and reformulating structured data. |
| Controlling excessive crawling at the server level | High | Helps conserve resources, but blocking can reduce visibility if it is not done selectively. |
| Avoid Client-Side Rendering (CSR) for key content | High | LLMs don't run JS; SSR or plain HTML is better for the important stuff. |
| Create content specifically targeted at AIs—either exclusive to them or hidden from them (e.g. with GEOhat LLM ) | High | Reinforces context without affecting user experience. |
Use of data-nosnippet to prevent sensitive information from appearing in SERPs | High | Useful for protecting data, but limits visibility if abused. It should be combined with other obfuscation strategies. |
| Review logs to detect AI tracking | High | Allows decisions to be made regarding accessibility and bot control. |
| Like/Dislike Campaigns in ChatGPT | Low | It does not affect the ranking or the appearance of URLs. |
Use of llms.txt or ai.txt | Null | It is not standard and has no real effect on crawling or ranking. |
| Shopify–ChatGPT Agreement | Circumstantial | Situational benefit for Shopify stores; not applicable to everyone. |
Let’s look at the key ways AI can gather information from your website.

ChatGPT has a long-term memory derived from its training process, which includes the information it has been previously trained with, as well as knowledge accessible through the Internet.
However, ChatGPT may store information about the user unless the user changes this option in Settings > Personalization > Memory .
This way, in addition to the general information it retains over the long term, the model can use data from not only the current conversation but also previous interactions, with the goal of offering more tailored responses to each user.
This allows you to identify, for example, whether the person prefers shorter or longer answers, whether they require a more technical level or, on the contrary, more basic explanations (depending on the topic). You can also adjust your writing style to the user's comprehension ability and reading style.
Therefore, if a user frequently asks questions about vegan cooking and environmentalism, the system can consider this information when making product or service recommendations, in order to optimize the relevance and satisfaction of the response.
ChatGPT is expected to use different search engines on a non-exclusive basis, adjusting its selection according to the user profile, the nature of the query, and potentially the version of the model (GPT or specific LLM) used.
According to various industry colleagues, at various times they claim that ChatGPT uses Google results , others say Bing results .
According to ChatGPT, they contradict themselves by saying that they only do so through tools or that they use Bing with ChatGPT plus with navigation.
As a middle ground, we should be careful about what appears in the SERPs, since that information can be used directly by AI without accessing our site. In other words, systems can extract our information even if we block crawlers with robots.txt. To prevent sensitive information from appearing in SERPs, you can use the data-nosnippet (spanish link) attribute.
Even in ChatGPT5, you can view the JSON file of the thought process and queries ChatGPT performs to create a response. This could help us see, from different users, the most common research ChatGPT performs on queries that may be relevant to our business and act accordingly.
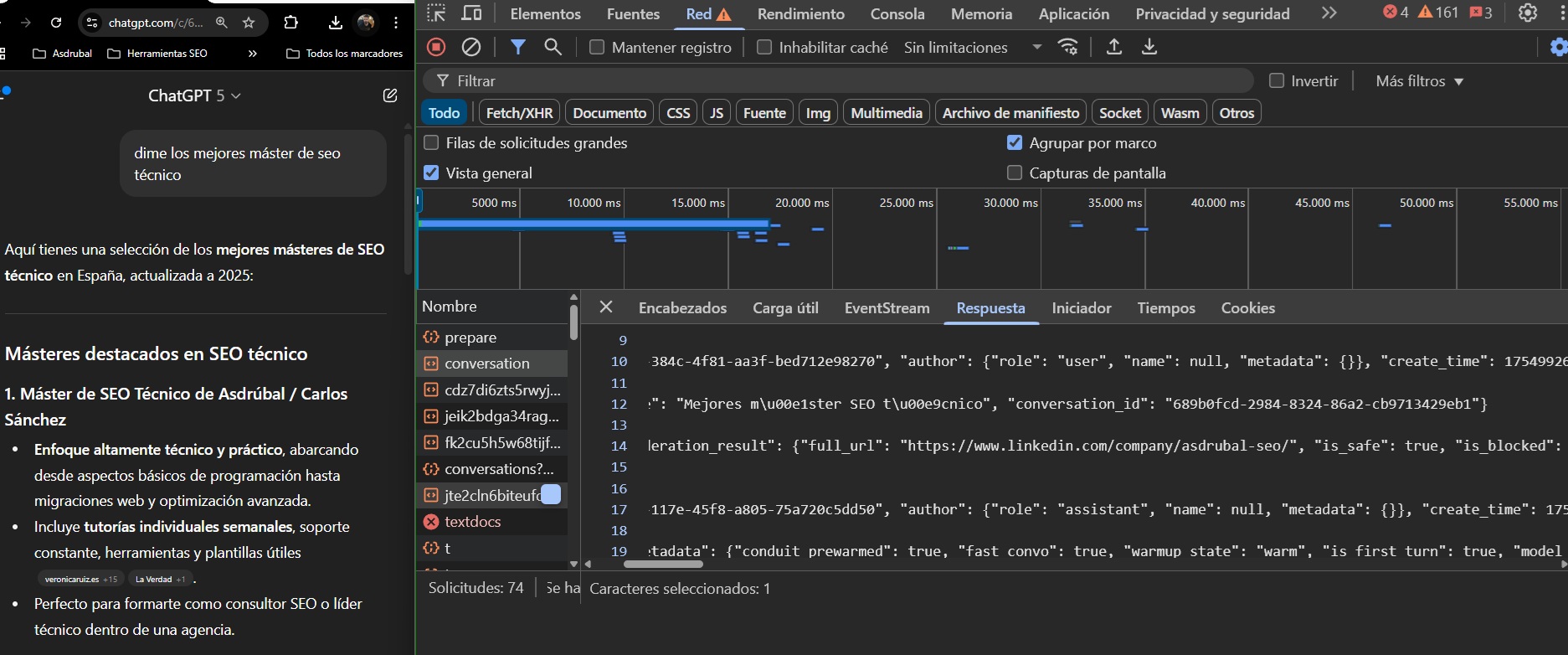
I will explain the step-by-step process to extract this information in my Technical SEO master's degree (just available in Spanish).
Most artificial intelligences, if we check the logs on several websites we've tested, respect it. However, we have the disadvantage I mentioned in the SERPs. Beyond that, many people enter user agents or rules incorrectly.
Then there would be the debate about whether it is appropriate to block information from LLMs that our competitors do provide.
Since the rise of artificial intelligence, web crawling has increased exponentially. This is due both to the language models themselves as they learn, and to user queries. Or to users who develop their own new AI tools or implement automations, significantly increasing web crawling.
Alvaro Fontela mentioned that it's starting to be a problem on servers , and it's normal that CEOs of hosting companies and CDNs like Cloudflare are making the decision to curb the activity of artificial intelligences through the server.
However, you need to be careful, especially if these cuts are made without your prior knowledge, because you could be missing out on the opportunity to improve your ranking in these LLMs.
The best and most recommended thing to do is to consult your hosting provider and check access to your website by changing the user agent to the usual ones for the AIs (you can do this with devtools ) to check if they are blocking AIs that are interesting to you.
You also have to know how to see the other side of the coin and check that so many AIs are not taking down your website.
If this is the case, it will always be better to block from the server than through robots.txt.

Another layer of complexity of SEO these days is that while we had managed to get Google to render JavaScript and be able to read our content, Artificial Intelligences today do not do so.
It's much more expensive to crawl websites with JavaScript , and they already achieve their purpose without doing so. Why would they spend more money at a loss just to be able to access your website when users are satisfied?
So CSR is not a good option for positioning in LLMs.
Another aspect we've been able to verify is that ChatGPT follows hreflang similar to Google. Even if it supposedly accesses the page in one language, it can show you content that's only available in the alternative version of the other language without telling you that it crawled that other part.
On my website, for example, it says that the sources are the about me page in English, but it shows me information that is only on the about me page in Spanish.
Although I don't want to lose focus since most of the work in this is doing traditional SEO tasks well, in fact in AI Overview it is almost everything, there are important aspects to take into account.

Javier Bermudez told me about four verticals he recommended to a stressed colleague, who, despite being an SEO, didn't know where to start to optimize GEO.
Then he raised the issue to be taken into account:
Accessibility audit
Make sure the server doesn't block AI bots, identify them, see what log analysis tools you're going to use, data governance on what you want the AI to have access to or not, review the HTML and CWVs to determine that the AI crawls and understands the content well.
Visibility audit
Use tools like Ahrefs' Brand Radar , SEranking's AI Search Toolkit , or more homemade tools and determine the starting point, what information the LLMS have about you.
Analytics Audit
How AI is attributed in your GA4, establish funnels, AI assistance with conversions on other channels, analysis of logs of the time when you publish and the AI tracks or mentions it, define success KPIs linked to accessibility/visibility/conversion factors
Work projection
Content improvement, link building, mentions, and everything that's more traditional SEO.
I'll present it as is, as a good roadmap that it is, but we must take into account the following aspects that are specific to LLMs more than traditional SEO (which, I repeat, is the majority).
Although there are multiple types of artificial intelligence—visual, conversational, predictive, generative—general LLMs (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Mistral) currently have the greatest weight in information queries.
These models work on large volumes of text and tend to provide quick and cost-effective responses without processing more complex formats such as video or audio, unless they already have a prior transcription in their training.
So:
On the other hand, traditional KW research can serve as a guide or to understand the business, not as a "manual bible to follow", however we can carry out measurable and objective "actions" that help us improve both in traditional SEO, and to help AIs better understand our content, we can do this for example by identifying semantically similar pages with Screaming frog .
I've never been a big fan of link building , and I thought Google would gradually lose its importance. That's true. But now LLMs do take something into account, and it's not so much the links, which are influential and, above all, can bring qualified traffic, but the mentions of you by others (without a link) can be key for LLMs to consider you as an authority.
So, when you do link building, if you do it, be very careful to mention the brand or product, so that you can be accessed with that information thanks to branding without the need for a link.
Both for your page and for content that others publish about you.
These are some tips that might work for you, and we've seen a substantial improvement in user acquisition through LLMs, plus a branding component that we can't measure:
In all other aspects, as with traditional SEO for Google, clear, structured, and unambiguous text helps the model process it correctly.
Irony, sarcasm, and double entendres tend to be misinterpreted by LLM and can lead to the main idea being missed or omitted. This is reminiscent of the era of "negative" clickbait on Google, where ironic headlines weren't always understood as such and served to improve rankings; in this case, they can work against you.
In any case, the rest of the content optimizations would be exactly the same as those that work in traditional SEO.
However, some of these tips may be a bit difficult to put on your website for all users to see. That's why I created a plugin of my own, called GEOhat LLM, that allows you to:

Let's see what stories there are
They've never worked, they're not a standard, and they're never expected to work. People persist in using them, even though spokespersons for various companies that offer these LLMs claim they do, and yet it's proven otherwise.
People like the easy way out, and it's quite common to see websites with plugins of this type that don't really work or serve any purpose.
It doesn't provide context or improve anything. ChatGPT doesn't crawl your website to see where it finds information. If you ask it about a product, it'll go to the product page, and if you ask about the company, it'll go to the "about us" section, the "legal information," and the logical places where your information is.
If you need to provide context for the website to be understood, either you have it in CSR and that's why it's not read, or your website needs content optimization.
Neither llms.txt nor ai.txt work.
And the truth is that it makes sense that they don't use it.
Each source interprets the correct llms.txt with different magical purposes and desires.
Some say it's to indicate the importance of the pages, others say it's to indicate whether or not they are allowed to train the model and what to do on the website using different directives, and others to offer a quick and detailed summary of what's on the website.
In either case, let's take the standard of indicating the pages as the correct one, as if it were a Sitemap (which already exists) but for LLMs with some more indication.
Why would you take the guidelines if you have your own navigation bar and search results on different search engines for your queries?
The reality is that they don't need it and it doesn't help them or the users at all.
It seems more like something designed for investors and those interested in buying shares in these two giants and then selling them before they fail. But in principle, it's an agreement where Shopify products will be integrated directly into ChatGPT, where openAI will take a commission.
It practically looks like an affiliate.
However, even though there is a beta version, we don't know if it will be well-received by users and work or fail, but it's possible that Shopify will have a short-term competitive advantage over ChatGPT in exchange for paying OpenAI a commission on sales.
Why do I think it will work less? I think users will eventually pass on products from websites they're interested in to ChatGPT (whether they're on Shopify or not) and ask for advice or recommendations.
People still use Google as a search engine, and ChatGPT more as an advisor and comparator. People like to feel like they're comparing and deciding.
In any case, this is my subjective opinion; none of us are futurologists, and we'll have to see how it develops. However, the agreement exists and is real. Although no exact or official date has yet been announced.
The "like" or "dislike" system in ChatGPT does not improve a website's ranking or alter the visibility of content in the results it offers to other users.
These buttons are used to:
What they don't do:
In short: liking or disliking serves to improve the user experience and quality of service, but it's not a trick to improve SEO or a website's ranking on ChatGPT.
That is to say, although it sounds easy and nice, unfortunately it doesn't work much.
OpenAI doesn't process individual votes one by one to modify outputs; instead, it aggregates large volumes of data and reviews them in a controlled manner. This makes it virtually impossible to "game" the system with a coordinated dislike campaign.
However, if you think a small-scale query might work, you have nothing to lose by trying this type of campaign.
On August 4th, Metehan Yesilyurt published an article titled " Breaking: Perplexity's 59 Ranking Patterns and Secret Browser Architecture Revealed (With Code) ".
The article is somewhat long, and I'll leave it there for anyone who wants to dig deeper. However, aside from a few peculiarities, the most important points only reinforce what has been said before. Let's go to what I consider the key points of your article:
This is undoubtedly the most distinctive feature and the one that caught my attention the most. Here are their tips:
You should update regularly and add new information to avoid ranking declines. Apparently, Perplexity quickly demotes what it considers "old" or "outdated."
I remember we have a generous embedding tutorial made by Juan Gonzalez Villa that he made for our Technical SEO master's degree .
That is, avoid duplicate, superficial content and negative feedback as much as possible.
LLM responses improve when supported by a strong internal linking structure to related articles to maintain semantic authority.
Yes, I've already mentioned Link Building, but since this section is a summary of Metehan's article, I have to include it, since he has also given it quite a bit of importance.
The article includes a list of "whitelist" domains that might be worth opting out of. Spoiler: it has always been the case.
SEO for LLMs (AIO/GEO) doesn't replace traditional SEO, but it does require understanding how artificial intelligence—especially ChatGPT—obtains and processes information. These models don't always crawl your website; they may rely on what appears in the SERPs; they generally respect robots.txt but don't execute JavaScript; and they value mentions and clear context more than pure links. Optimizing for them involves ensuring accessibility to key information, controlling visibility and branding, and creating structured, comparative, and unambiguous textual content.
Myths like the use of llms.txt or manipulating likes/dislikes don't work to improve rankings. The focus should be on good technical SEO, adapting content to the format that AIs understand, and strategically managing the access granted to them, while keeping in mind that the majority of the effort still lies in traditional web optimization.
I currently offer advanced SEO training in Spanish. Would you like me to create an English version? Let me know!
Tell me you're interested